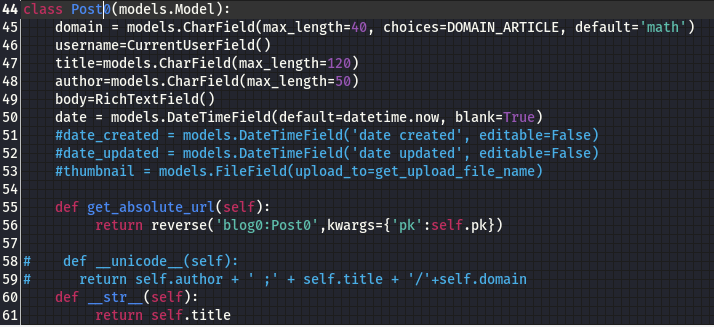
Web Application
Web application is a software program that runs on a web server and is accessed through a web browser over a network such as the Internet or an intranet. Unlike traditional desktop applications which are launched by your operating system, web apps must be accessed through a web browser.
Web applications use a combination of server-side scripts (PHP, Python, etc.) to handle storage and retrieval of information, and client-side scripts (JavaScript, HTML) to present information to users.
- Accessible from any device with a web browser
- No installation or downloads required
- Automatic updates for all users
- Centralized data storage and backup
Common examples of web applications include online banking, social media platforms, e-commerce websites, web-based email clients, and online office suites. These applications have revolutionized how we work, communicate, and conduct business in the digital age.
Types of Web Applications
Static Web Applications
These are the simplest type of web applications. They display the same content for every user and are built using HTML and CSS. They're ideal for portfolio websites or landing pages.
Dynamic Web Applications
These applications generate content in real-time based on user requests. They use server-side programming and databases to deliver personalized content to each user.
Progressive Web Apps
PWAs combine the best features of web and mobile apps. They work offline, send push notifications, and can be installed on devices while still being delivered through the web.
Benefits of Web Applications
For Businesses
- Cost-effective: Lower development and maintenance costs compared to native applications
- Easy maintenance: Updates can be applied directly to the server without user intervention
- Accessibility: Reach users on any platform or device
- Scalability: Easy to scale up or down based on demand
For Users
- No downloads: Access instantly through a web browser
- Always updated: Always use the latest version
- Platform independent: Works on Windows, Mac, Linux, mobile devices
- Storage saving: No local storage required
Web Application Architecture
Web applications typically follow a three-tier architecture:
Presentation Layer (Frontend)
This is the user interface that runs in the web browser. It's built using HTML for structure, CSS for styling, and JavaScript for interactivity.
Application Layer (Backend)
This layer contains the business logic and processes user requests. It's built using server-side languages like Python, PHP, Java, or Node.js.
Data Layer (Database)
This layer stores and manages all application data. Common databases include MySQL, PostgreSQL, MongoDB, and Oracle.
Security considerations: Web applications must implement proper security measures including HTTPS encryption, input validation, authentication and authorization, session management, and protection against common vulnerabilities like SQL injection and cross-site scripting (XSS).
